How to Reduce E-Commerce Overhead

By Neil Patel
We’re well into the digital age, and e-commerce stores are more prevalent than ever. There are an estimated 12 million to 14 million online stores worldwide—and those numbers grow every day.
The popularity of online stores makes sense. With just a few hundred dollars, you can have a fully-functioning online business.
While online stores tend to have fewer expenses, e-commerce overhead can quickly add up. As a business owner, you should always be looking for ways to cut costs.
Where do you start?
Which costs can you forgo, and which do you need?
How can you ensure you’re not stunting your business’ growth?
That is what this article will cover. Let’s look at the most effective ways to reduce your online store costs.
What Are E-Commerce Overhead Costs?
Overhead is an accounting term that refers to most business-related expenses.
Investopedia explains,
Overhead refers to the ongoing business expenses not directly attributed to creating a product or service.
Many people mistake their operating expenses for overhead costs. However, these are not the same.
Here’s how to tell the difference:
Operational costs are any expenses that help you run the day-to-day operations of your business. For an e-commerce store, these include the materials you buy, labor, production, packaging, shipping, marketing, and other related costs.
On the other hand, overhead costs are ongoing expenses that you incur whether or not you’re producing or selling anything. For an e-commerce store, these include insurance, software, web hosting fees, employee and management salaries, etc.
This graphic helps break it down a bit further:
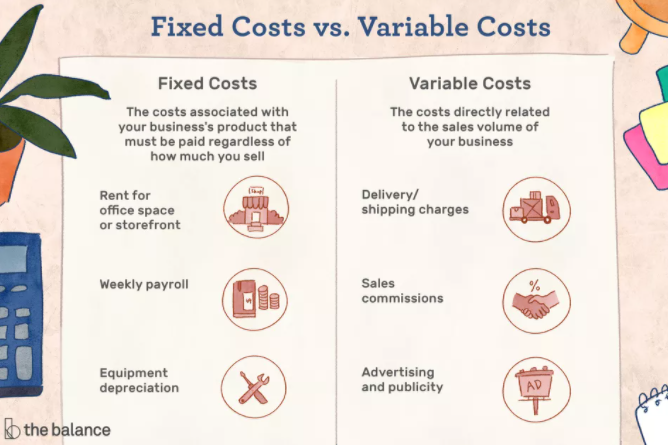
Before you can cut back on these expenses, you’ll need to divide them into different categories to understand what can be cut and what cannot.
You can divide your e-commerce overhead into three different categories:
1. Fixed Overhead Costs
As the name suggests, these costs are fixed and can’t be changed. For example, the warehouse rent you pay every month.
2. Variable Overhead Costs
This refers to expenses that differ from month to month, such as an electricity bill. The electric bill might be higher during certain times of the year (like winter or summer) and lower at other times. There is no fixed month to month payment.
3. Semi-Variable Overhead Costs
Semi-variable costs mean that a portion of the payment is fixed, while the other part may depend on your activities. For instance, your email marketing platform may have a base charge to pay every month and then another charge based on how many emails you send or how many contacts you have.
To reduce your e-commerce overhead, focus on your variable and semi-variable costs because these are the expenses that can be cut back on with a little planning and strategy.
Predicting E-Commerce Overhead Costs and Setting a Budget
It’s challenging to reduce costs when you don’t …read more
Source:: Kiss Metrics Blog








